The Funtoo Linux project has transitioned to "Hobby Mode" and this wiki is now read-only.
Difference between revisions of "Package:IBus"
m (Omasanori moved page Ibus to Package:IBus: To align with other package description pages) |
(Add ebuild information) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Ebuild | |||
|Summary=Intelligent Input Bus for Linux / Unix OS | |||
|CatPkg=app-i18n/ibus | |||
|Homepage=https://github.com/ibus/ibus/wiki | |||
}} | |||
IBus(Intelligent Input Bus) is an input method(IM) framework that uses a bus-like architecture. It's widely used in the Linux desktop world and is integrated in desktop environments like '''Gnome'''. It allows for different plugins to be installed for input in different languages, this modular design + compatibility with XKB and desktop environments makes ibus the preferred choice for people typing in CJK(Chinese Japanese Korean), Vietnamese, Thai and other languages that require specific tools not found in standard XKB. | IBus(Intelligent Input Bus) is an input method(IM) framework that uses a bus-like architecture. It's widely used in the Linux desktop world and is integrated in desktop environments like '''Gnome'''. It allows for different plugins to be installed for input in different languages, this modular design + compatibility with XKB and desktop environments makes ibus the preferred choice for people typing in CJK(Chinese Japanese Korean), Vietnamese, Thai and other languages that require specific tools not found in standard XKB. | ||
== Installation == | == Installation == | ||
Revision as of 23:57, September 1, 2022

IBus
We welcome improvements to this page. To edit this page, Create a Funtoo account. Then log in and then click here to edit this page. See our editing guidelines to becoming a wiki-editing pro.
IBus(Intelligent Input Bus) is an input method(IM) framework that uses a bus-like architecture. It's widely used in the Linux desktop world and is integrated in desktop environments like Gnome. It allows for different plugins to be installed for input in different languages, this modular design + compatibility with XKB and desktop environments makes ibus the preferred choice for people typing in CJK(Chinese Japanese Korean), Vietnamese, Thai and other languages that require specific tools not found in standard XKB.
Installation
| +X | Adds X11 support |
| appindicator | Builtin support for notifications using the libindicate or libappindicator plugin |
| +emoji | Enables emoji support |
| gtk2 | Enables GTK-2 input method module |
| +gtk3 | Enables GTK-3 input method module |
| gtk4 | Enables GTK-4 input method module |
| +gui | Enables support for a graphical user interface |
| +introspection | Adds support for GObject based introspection |
| nls | Adds Native Language Support(using gettextGNU locale utilities) |
| +python | Adds optional support/bindings for the Python programming language |
| test | Enable dependencies and/or preparations necessary to run tests (usually controlled by FEATURES=test but can be toggled independently) |
| +unicode | Enables support for Unicode choice |
| vala | Enables bindings for dev-lang/vala |
| wayland | Enables dev-libs/wayland backend |
Installing ibus is as simple as:
root # emerge ibus
once ibus is installed, you can use it as is because it is interoperable with XKB, or you can install tables and plugins to add additional language support if needed.
Integrating ibus into your Desktop Environment
Gnome and Gnome-based desktops support ibus out of the box so you don't have to configure anything
For KDE the ibus USE flag needs to be enabled for the following packages:
- qtgui
- plasma-desktop
For all desktops you are going to need to add the following code to your ~/.xinitrc or ~/.xprofile
~/.xprofile or ~/.xinitrc (sh source code) export XMODIFIERS=@im=ibus
export GTK_IM_MODULE=ibus
export QT_IM_MODULE=ibus
export SDL_IM_MODULE=ibus
export GLFW_IM_MODULE=ibus
ibus-daemon -drx
The environment variables will be read by applications which will enable ibus support, the last line starts the ibus-daemon so that you don't have to start it manually
Using the ibus interfaces
Once ibus is installed, normally there will be 2 ways to interact with it, the ibus CLI and the ibus-setup GUI
IBus CLI
The ibus command provides multiple ways of interacting with ibus, for example:
user $ ibus engine
will list the current active ibus engine
user $ ibus engine libpinyin
will set the current ibus engine to libpinyin
user $ ibus list-engine
will list all available engines for every language category, while the control arguments of
- start
- restart
- exit
will control the state of the ibus daemon
For more information refer to the ibus wiki
IBus GUI
On some desktops such as Gnome where ibus is integrated into the desktop environment, you might get the IBus settings integrated into your settings manager, these settings however are not as full as the ones provided by the official IBus GUI settings manager, ibus-setup
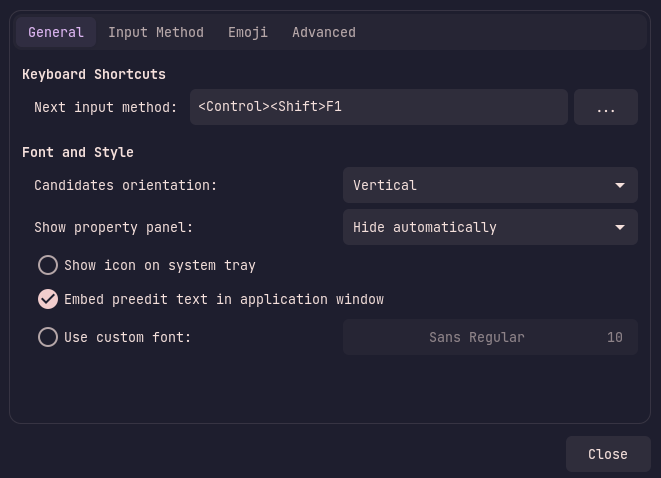
To open it, run the command ibus-setup and a window like this should appear:
Under the General tab you can find common settings such as the IM switching keybing and font settings
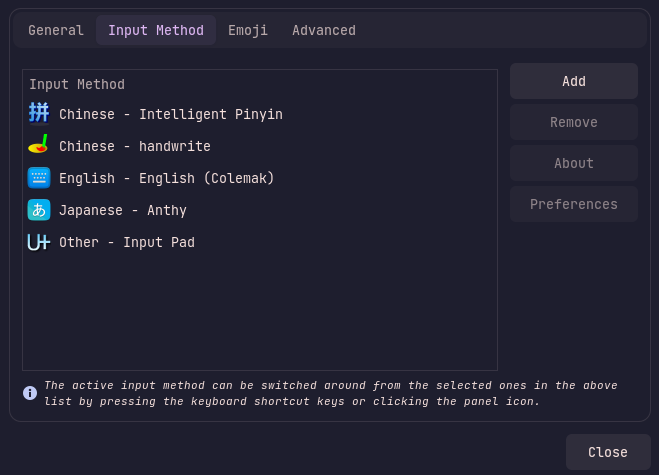
Under the Input Method tab you can find your current input methods. On the side panels you can add, remove, access the settings or information about a given input method. Here is an example image:
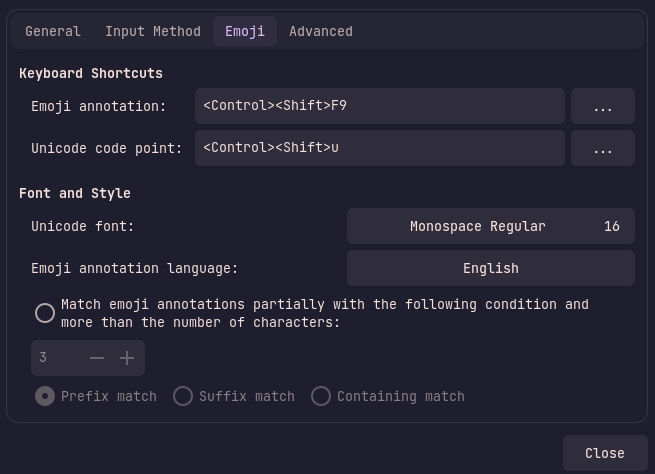
When compiled with the default USE flags, ibus provides emoji input and settings under the Emoji tab, Example image below:
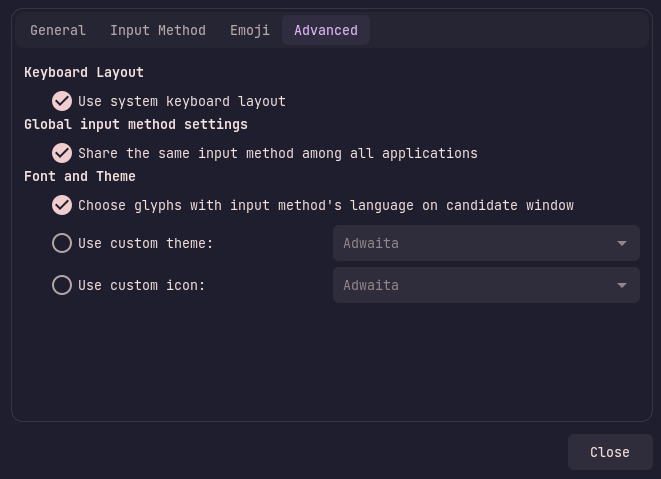
Finally in the Advanced tab you can find settings that allow you to change the theme of the IBus GUI, as well as settings on whether to use the system keyboard layout, and whether to share the input method among all applications:
If you depend on running a custom keyboard layout in XKB that isn't available by default in both XKB and ibus, you are going to need to use both systems for input. To do that make sure that the settings Use system keyboard layout and Share the same input method among all applications are enabled, otherwise you will notice how your layout changing shortcut in XKB, doesn't switch to your languages set in your XKB settings
IBus plugins in Funtoo
Funtoo provides multiple packages for different language support in IBus, for more information please open the separate wiki pages listed below: