The Funtoo Linux project has transitioned to "Hobby Mode" and this wiki is now read-only.
Installation (Tutorial)
If you want to do a standard Funtoo Linux installation, I recommend you use the shorter, official Funtoo Linux Installation Instructions instead. -Daniel
This document is unmaintained, and probably out of date.
This page has been proposed for deletion because it does not meet the Editing Guidelines.
If you disagree, please discuss it here.
Introduction
This HowTo aims to give the experienced GNU/Linux User a quick way to install Funtoo Linux in a nice and fast way. Also we will give you all the necessary steps for installing Funtoo GNU/Linux in this guide, but we won't go deeper into the details of them as need
There are two ways of installing Funtoo GNU/Linux on your PC:
- using an already installed GNU/Linux System or
- using a LiveCD
If you plan to use a LiveCD, we recommend you to use SystemRescueCd.
All the commands in this guide are performed as "root", unless we indicate it otherwise.
This HowTo will cover the following four setups:
- a standard Installation (MBR, HDD not encrypted),
- a standard secure Installation (MBR, HDD encrypted),
- a modern Installation (GPT/GUID partition table, HDD not encrypted) and
- a modern secure Installation (GPT/GUID partition table, HDD encrypted).
These four approaches have the following Pros and Cons:
| Setup | Pro | Contra |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |
|
|
| 2 |
|
|
| 3 |
|
|
| 4 |
|
|
With the help of the the above table you should be able to select your future Hard Disk (HDD) partitioning scheme. In the further guide we will go through every single step for all four schemes.
For booting your old/other GNU/Linux System we won't give you a special detailed howto guide, as you should know how to do so, as concerning the booting with SystemRescueCd, we will give you a short step-by-step guide on how to boot up the system.
This guide will only be split into subparts for the installation process if concerning the four above mentioned steps, here the split points will be MBR vs. GPT/GUID-partitioning and encrypted vs. unencrypted HDD. So be aware of these parts if you want to use them.
Booting the Installation System
Booting old/other GNU/Linux
This step is really simple, as you know your old GNU/Linux System and you need simply start your Computer, select in the boot-loader your GNU/Linux System, let it start up, log in as always and start a root-terminal.
Booting with SystemRescueCd
First step is to download SystemRescueCd, an overview of the actual version can be found at http://www.sysresccd.org/Download, just follow there the link to the Sourceforge Download, you will download then about 300 MB to your HDD. If finished burn this ISO-image with your favorite burning tool like burn-cd, bashburn, K3B, GNOMEbaker on a GNU/Linux Box or NERO Burning ROM, CDBurnerXP Pro, and many more on a Microsoft® Windows™ box.
Next insert this CD into your CD-ROM-Drive and boot up the PC with it where you want to install Funtoo GNU/Linux. Make sure you boot from the CD when booting. The Booting process with SystemRescueCd will follow the next steps:
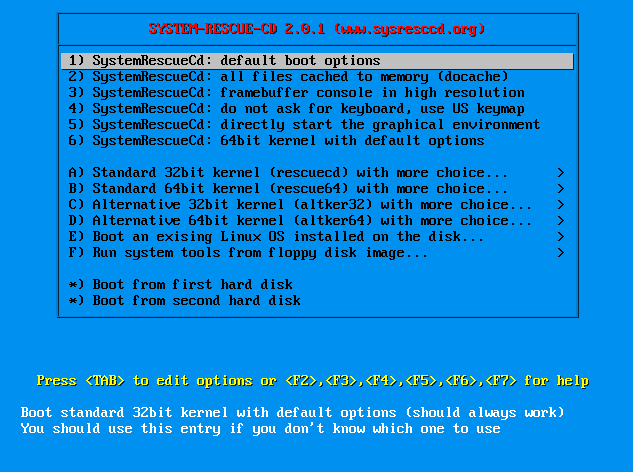
- Selecting your Kernel to boot SystemRescueCd with:
In that screen you will be greeted with all the power of SystemRescueCd, depending on your CPU we use the boot option 1) for a 32-bit CPU or a 64-bit CPU that should run in 32-bit mode and 6) for a 64-bit CPU in 64-bit mode. If this boot option fails, use the boot option A) or B), will will lead to the following screen:
That menu will give you more boot options. If you select 1. here, it would be the same kernel option like in the previous screen 1) and 6). The next step is to select your keyboard layout for installation.
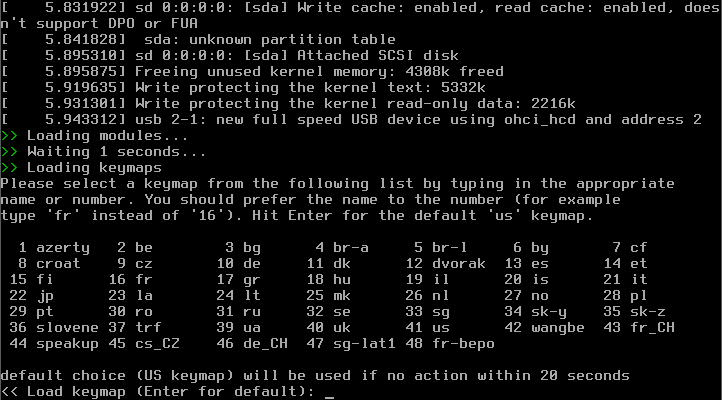
- Selecting your Installation Keyboard Layout
That step requires a bit of your atention, as it only gives you 20 seconds time to choose your keyboard layout, if you are OK with the US keymap, just press Enter to accept the default setting.
- Being ready
Seconds later SystemRescueCd welcomes you wit a short message and is ready fo you to be used to perform your installation.
HDD Preparation
As mentioned earlier in this guide we cover four different installation variations, the could be displayed in an installation matrix as below:
| MBR | GPT | |
|---|---|---|
| unencrypted | See MBR | See GPT/GUID partition table |
| encrypted | See MBR | See GPT/GUID partition table |
If you are going to plan to install Funtoo GNU/Linux on a machine where another O/S is already installed, you have to make some free space available on your HDD in order to do so. A resize of most existing filesystems can be done with SystemRescueCd too. You just need to enter the graphical environment and use gparted. We will give you a short example on how to do so with a sample HDD that might hold windows, so you get a feeling what to do, but be aware that a resize can be a dangerous part, so please keep a backup of your data, as Funtoo Technologies wouldn't take any responsibility for a loss of data that could happen by the process of shrinking a partition.
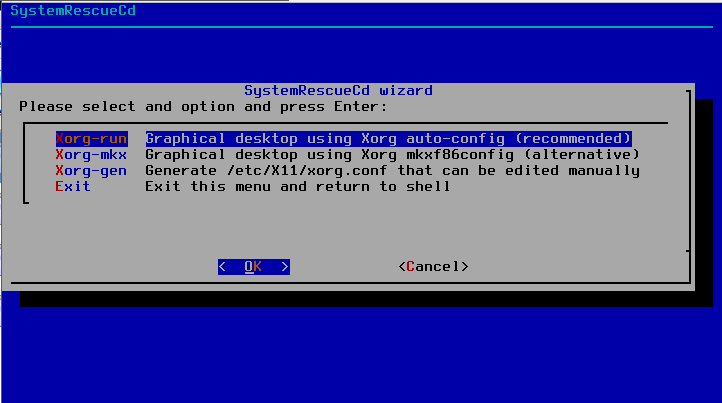
Starting the graphical environment in SystemRescueCd is really simple, just execute the following command:
root@sysresccd /root % wizard
and it will start a dialog for the graphical environment setup, for most users the default options should be OK. Both the dialog and the graphical environment (Xfce) are shown in the next two images.
Resize of HDD partitions
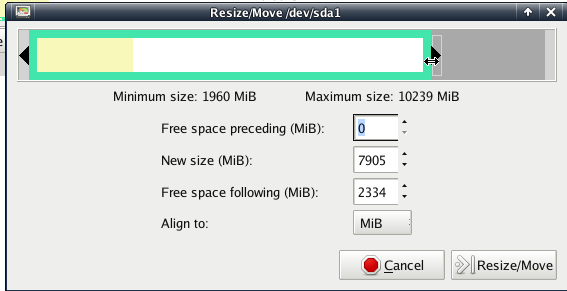
The above screen shows us that there is the tool called GParted right on the frontpanel. That tool will be used to resize our HDD partitions. The following screen shows us an example of how the tool looks if you start it.
By clicking on the partion you want to resize you make it active right-click on it and use the point resize and you will see the Resize/Move dialog, here you can edit the resize options for that partiton.
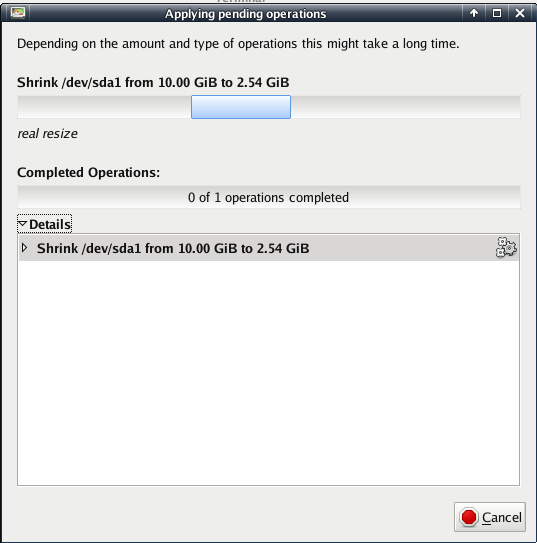
When you finished setting the resize options, you will see that the grey-green hook in the menu got green, that means you have jobs added to the working list. If you have all actions done on the partition, click on the green hook and your resize action will run by giving you the following feedback window:
when that has finished you will see the resized result and it should look like that:
we are finished with resizing the dis partitions, exit the Tool and close Xfce by clicking the running exit man in the down right. We are back on the command line and are ready to partitions our disk. to our needs, for a unified way we will show it with an empty partition table, so if you have resized some partitions, they will be listed in the MBR menu, as if you want to use an GPT/GUID partition table we will start from a clean table anyway.
Partitioning scheme
If you are partitioning the hard drive of a SPARC machine, please see Funtoo Linux Installation on SPARC. Also, note that OpenBoot has no support for GPT volumes and you won't be able to boot on the system volume if that later has been partitioned with GPT.
For partitioning we suggest the following schemes:
- MBR unencrypted
| Partition | Size | fdisk option | Filesystem (FS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| /boot | 200 MB | 83 | ext2 |
| swap | 2x RAM if 1024 MB or less, otherwise 2 GB | 82 | sw (default) |
| / | 20-50 GB | 83 | ext4 |
| /usr/portage | ~10 GB | 83 | ext4 |
| /home | As much as possible. | 83 | xfs |
- MBR encrypted
| Partition | Size | fdisk option | FS |
|---|---|---|---|
| /boot | 200 MB | 83 | ext2 |
| cryptoroot | Rest of the Disc | 83 | none |
- GPT unencrypted
| Partition | Size | gdisk option | FS |
|---|---|---|---|
| /boot | 200 MB | 0700 | ext2 |
| EFI-Boot | 512 kB | EF02 | none |
| swap | 2x RAM if 1024 MB or less, otherwise 2 GB | 8200 | swap (default) |
| / | 20 - 50 GB | 0700 | ext4 |
| /usr/portage | ~10 GB | 0700 | ext4 |
| /home | Rest of the Disc | 0700 | xfs |
- GPT encrypted
| Partition | Size | gdisk option | FS |
|---|---|---|---|
| /boot | 200 MB | 0700 | ext2 |
| EFI-Boot | 512 kB | EF02 | none |
| cryptoroot | Rest of the Disc | 0700 | none |
MBR
Now we will partition the HDD using the above scheme with a disk partitioning tool named "fdisk". So just invoke it with the following command:
# fdisk /dev/sda
it will greet you like this
by pressing `m` you will get a help context menu that will give you the following options:
a toggle a bootable flag b edit bsd disklabel c toggle the dos compatibility flag d delete a partition l list known partition types m print this menu n add a new partion o create a new empty DOS partition table p print the partition table q quit without saving changes s create a new empty Sun disklabel <--- SPARC specific, see Funtoo installation notes for SPARC t change a partition's system id u change display/entry units v verify the partition table w write table to disk and exit x extra functionality (experts only)
The partitioning scheme is created with the following commands inside of fdisk:
unencrypted
Command (m for help): n
it will ask you now if you want to add a primary or extended partition, we choose primary by pressing
Command action e extended p primary partition (1-4) p
and use for the next 2 steps the default options and add as the Last Sector for the first partition the following:
Partition number (1-4, default 1): (default) Using default value 1 First sector: (Use default) Using default value Last sector, ...: +200M
your input should look like that right now:
next we need to make the partition bootable and add then the rest of the partitions:
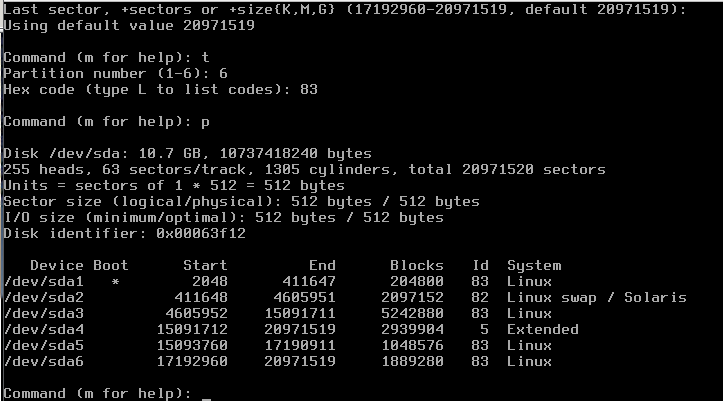
Command (m for help): a Partition number (1-4): 1 Command (m for help): t Selected partition 1 Hex code (type L to list codes): 83 Command (m for help): n Command action e extended p primary partition (1-4) p Partition number (1-4, default 2): (default) Using default value 2 First sector: (Use default) Using default value Last sector, ...: +2G Command (m for help): t Partition number (1-4): 2 Hex code (type L to list codes): 82 Changed system type of partition 2 to 82 (Linux swap / Solaris) Command (m for help): n Command action e extended p primary partition (1-4) p Partition number (1-4, default 3): (default) Using default value 3 First sector: (Use default) Using default value Last sector, ...: +20G Command (m for help): t Partition number (1-4): 3 Hex code (type L to list codes): 83 Command (m for help): n Command action e extended p primary partition (1-4) e Selected partition 4 First sector: (Use default) Using default value Last sector, ...: (Use default) Using default value Command (m for help): n First sector: (Use default) Using default value Last sector, ...: +10G Command (m for help): t Partition number (1-5): 5 Hex code (type L to list codes): 83 Command (m for help): n First sector: (Use default) Using default value Last sector, ...: (Use default) Command (m for help): t Partition number (1-6): 6 Hex code (type L to list codes): 83 Command (m for help): p
this will result in the following output
now just write the partition table to your disk by using `w`, this will result in the following output:
Command (m for help): w The partition table has been altered! Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table. Syncing disks.
If that was your scheme, you are now so far to get to the partition formatting section.
encrypted
Command (m for help): n
it will ask you now if you want to add a primary or extended partition, we choose primary by pressing
Command action e extended p primary partition (1-4) p
and use for the next 2 steps the default options and add as the Last Sector for the first partition the following:
Partition number (1-4, default 2): (default) Using default value 1 First sector: (Use default) Using default value Last sector, ...: +200M
Next we need to make the partition bootable and add then the rest of the partition:
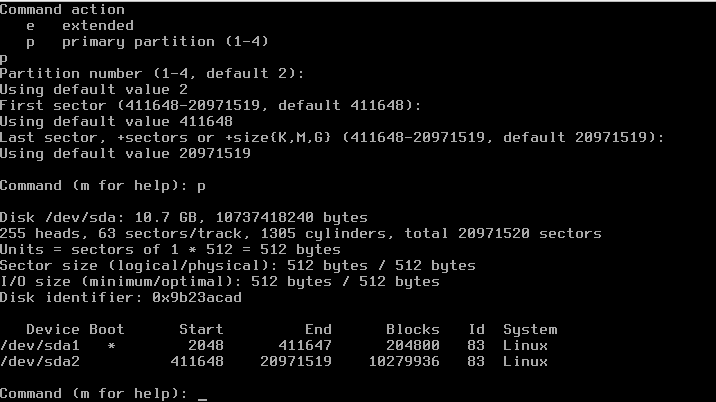
Command (m for help): a Partition number (1-4): 1 Command (m for help): t Selected partition 1 Hex code (type L to list codes): 83 Command (m for help): n Command action e extended p primary partition (1-4) p Partition number (1-4, default 2): (default) Using default value 2 First sector: (Use default) Using default value Last sector, ...: (use default) Command (m for help): p
this will result in the following output
now just write the partition table to your disk by using w, this will result in the following output:
Command (m for help): w The partition table has been altered! Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table. Syncing disks.
next we need to prepare our cryto-container that will keep all the encrypted stuff in it. For that, go to the Cryptocontainer section.
GPT/GUID partition table
This setup is for most users more intuitive, since we don't need to care about extended partitions. We only need to setup an extra partition for our bootloader. So let us do it for unencrypted and encrypted partitions.
For setting up the GPT partition table we use the tool "gdisk", that is the GPT equivalent of fdisk.
Just start it with the following command:
gdisk /dev/sda
it will greet you with the following screen
unencrypted
Next we will create the partitions for our unencrypted setup:
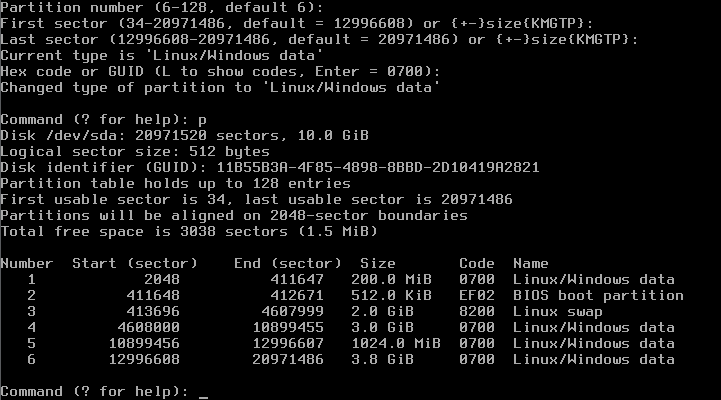
Command (? for help): n Partition number (1-128, default 1): (Use default) First sector (34-..., default = 34) or ...: (Use default) Information: Moved requested sector from 34 to 2048 in order to align on 2048-sector boundaries. Use 'l' on the experts' menu to adjust alignment Last sector (2048-..., default = ...) or ...: +200M Current type is 'Linux/Windows data' Hex code or GUID (L to show codes, Enter = 0700): (ENTER) Changed type of partition to 'Linux/Windows data' Command (? for help): n Partion number (2-128, default 2): (Use default) First sector (...) or ...: (Use default) Last sector (...) or (...): +512K Current type is 'Linux/Windows data' Hex code or GUID (L to show codes, Enter = 0700): ef02 Changed type of partition to 'BIOS boot partition' Command (? for help): n Partition number (3-128, default 3): (Use default) First sector (...) or ...: (Use default) Last sector (...) or (...): +2G Current type is 'Linux/Windows data' Hex code or GUID (L to show codes, Enter = 0700): 8200 Changed type of partition to 'Linux swap' Command (? for help): n Partition number 4-128, default 4): (Use default) First sector (...) or ...: (Use default) Last sector (...) or (...): +20G Current type is 'Linux/Windows data' Hex code or GUID (L to show codes, Enter = 0700): (ENTER) Changed type of partition to 'Linux/Windows data' Command (? for help): n Partition number 5-128, default 5): (Use default) First sector (...) or ...: (Use default) Last sector (...) or (...): +10G Current type is 'Linux/Windows data' Hex code or GUID (L to show codes, Enter = 0700): (ENTER) Changed type of partition to 'Linux/Windows data' Command (? for help): n Partition number 6-128, default 6): (Use default) First sector (...) or ...: (Use default) Last sector (...) or (...): (Use default) Current type is 'Linux/Windows data' Hex code or GUID (L to show codes, Enter = 0700): (ENTER) Changed type of partition to 'Linux/Windows data' Command (? for help): p
will now show you a disk partitioning like that one:
now write the table to your disk with w;
Command (? for help): w Final checks complete. About to write GPT data. THIS WILL OVERWRITE EXISTING PARTITIONS!! Do you want to proceed, possibly destroying your data? (Y/N): Y OK; writing new GUID partition table (GPT). The operation has completed successfully.
Now go the section about creating the filesystem on MBR.
encrypted
Next we will create the partitions for our encrypted setup:
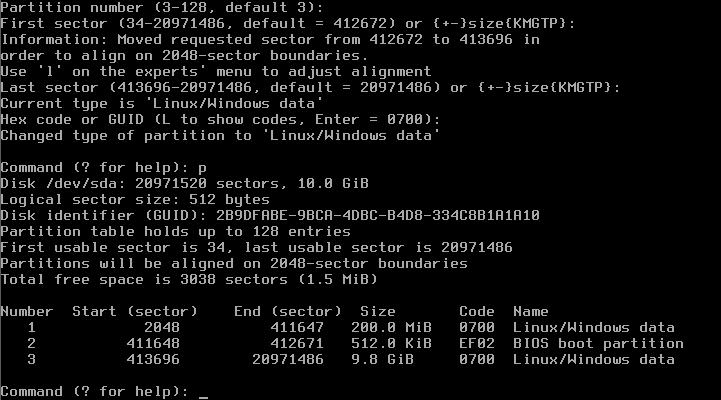
Command (? for help): n Partition number (1-128, default 1): (Use default) First sector (34-..., default = 34) or ...: (Use default) Information: Moved requested sector from 34 to 2048 in order to align on 2048-sector boundaries. Use 'l' on the experts' menu to adjust alignment Last sector (2048-..., default = ...) or ...: +200M Current type is 'Linux/Windows data' Hex code or GUID (L to show codes, Enter = 0700): (ENTER) Changed type of partition to 'Linux/Windows data' Command (? for help): n Partion number (2-128, default 2): (Use default) First sector (...) or ...: (Use default) Last sector (...) or (...): +512K Current type is 'Linux/Windows data' Hex code or GUID (L to show codes, Enter = 0700): ef02 Changed type of partition to 'BIOS boot partition' Command (? for help): n Partition number (3-128, default 3): (Use default) First sector (...) or ...: (Use default) Last sector (...) or (...): (Use default Current type is 'Linux/Windows data' Hex code or GUID (L to show codes, Enter = 0700): (ENTER) Changed type of partition to 'Linux/Windows data' Command (? for help): p
will now show you a disk partitioning like that one:
now write the table to your disk with w;
Command (? for help): w Final checks complete. About to write GPT data. THIS WILL OVERWRITE EXISTING PARTITIONS!! Do you want to proceed, possibly destroying your data? (Y/N): Y OK; writing new GUID partition table (GPT). The operation has completed successfully.
Now go to the Cryptocontainer setup.
Cryptocontainer
Setting up the cryptocontainer for our encrypted system is in both cases nearly identically, but for the easier showing effect we will give both examples in a seperate subsection.
MBR
First we will prepare the HDD for being encrypted, if you use SystemRescueCd in version 2.0.1 or higher just execute the following commands:
If you want to see progress of dd than you have to open another terminal and execute: kill -s USR1 `pidof dd`
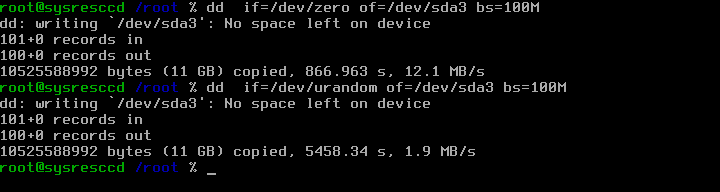
# dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sda2 bs=100M # dd if=/dev/urandom of=/dev/sda2 bs=100M
This part is optional but for security reason we advise you to do so if you like to have a secure encrypted disk. This part takes a lot of time, let your Computer run and get out to sleep and work, as it might take a day or two depending on your HDD size. :)
You should also be aware that you will get a hint about reaching the end of your HDD. That's intended and desired in this case so that the command can work without knowing your disk-size.
If you ran the above commands you should see an output similar to the one shown in the screenshot:
Next we need to encrypt our HDD, that will be done with the following commands:
# cryptsetup -c aes-xts-plain luksFormat /dev/sda2 WARNING! ======== This will overwrite data on /dev/sda2 irrevocably. Are you sure (Type uppercase yes): YES Enter LUKS passphrase: (Your paranoid passphrase) Verify passphrase: (Your paranoid passphrase again)
Then we need to mount our HDD:
# cryptsetup luksOpen /dev/sda2 dmcrypt_root Enter passphrase for /dev/sda2: (your paranoid passphrase)
Next we will creat the logical volumes for our setup, so have a look at the subsection about logical volumes.
GPT/GUID
This section is nearly the same as above, so if you read the text in one you will reread the MBR section again only with the GPT enabled stuff.
If you want to see progress of dd than you have to open another terminal and execute: kill -s USR1 `pidof dd`
First we will prepare the HDD for being encrypted, if you use SystemRescueCd in version 2.0.1 or higher just execute the following commands:
# dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sda3 bs=100M # dd if=/dev/urandom of=/dev/sda3 bs=100M
This part is optional but for security reason we advise you to do so if you like to have a secure encrypted disk. This part takes a lot of time, let your Computer run and get out to sleep and work, as it might take a day or two depending on your HDD size. :)
You should also be aware that you will get a hint about reaching the end of your HDD. That's intended and desired in this case so that the command can work without knowing your disk-size.
If you ran the above commands you should see an output similiar to the one shown in the screenshot:
Next we need to encrypt our HDD, that will be done with the following commands:
# cryptsetup -c aes-xts-plain luksFormat /dev/sda3 WARNING! ======== This will overwrite data on /dev/sda3 irrevocably. Are you sure? (Type uppercase yes): YES Enter LUKS passphrase: (your paranoid passphrase) Verify passphrase: (your paranoid passphrase again)
Then we need to mount our HDD:
# cryptsetup luksOpen /dev/sda3 dmcrypt_root Enter passphrase for /dev/sda3: (your paranoid passphrase)
next we will creat the logical volumes for our setup, so have a look at the following subsection.
logical volumes
Feel free to adjust your sizes here, we will follow our given advices above for that. First we need to creat the the physical volume, then the volume group and at last the logical volumes. doing so is really easy, just do the following for if you want to follow our advices above:
# pvcreate /dev/mapper/dmcrypt_root Physical volume "/dev/mapper/dmcrypt_root" successfully created # vgcreate vg /dev/mapper/dmcrypt_root Volume group "vg" successfully created # lvcreate -L20G -nroot vg Logical volume "root" created # lvcreate -L2G -nswap vg Logical volume "swap" created # lvcreate -L10G -n portage vg Logical volume "portage" created # lvcreate -l 100%FREE -nhome vg Logical volume "home" created
filesystem creation
Now that we have created our partitioning scheme, we can go on to create the filesystems needed for our partitions. Here differences only occur between the unencrypted setups. Encrypted volumes are handled the same way, no matter whether MBR and GPT, so there is no need to split them up in two seperate parts:
MBR unencrypted
For the unencrypted partions in the MBR setup just use the following regarding to our above given adives, you may feel free to change some parts of it if you like:
# mkfs.ext2 /dev/sda1 # mkswap /dev/sda2 # mkfs.ext4 /dev/sda3 # mkfs.ext4 /dev/sda5 # mkfs.xfs /dev/sda6
That was all for having your filesystem created. now go to the System Setup.
GPT unencrypted
Now let us create the filesystem for our GUID partition table. It is as easy as above, just see the difference in the jump of partition name:
# mkfs.ext2 /dev/sda1 # mkswap /dev/sda3 # mkfs.ext4 /dev/sda4 # mkfs.ext4 /dev/sda5 # mkfs.xfs /dev/sda6
Next step is to mount our partitons, for that go to the System Setup.
MBR/GPT encrypted
If you choose to encrypt your HDD, you will in both cases follow the next steps to setup your filesystems:
# mkfs.ext2 /dev/sda1 # mkswap /dev/mapper/vg-swap # mkfs.ext4 /dev/mapper/vg-root # mkfs.ext4 /dev/mapper/vg-portage # mkfs.xfs /dev/mapper/vg-home
So far we prepared the disk and will now mount our partitions.
System Setup
Mounting filesystem
As we need to have a mountpoint for our system, we now create it with
# install -d /mnt/funtoo
The in the following used install -d command just creats all the needed folders for later mountpoints for us. If you like you can control it by using ls /mnt/funtoo after the install -d part. Now you are ready to install your base system, read on in Downloading the System.
MBR unencrypted
Now mount your system partitions like that if you used our above advice:
# swapon /dev/sda2
# mount /dev/sda3 /mnt/funtoo
# install -d /mnt/funtoo/{boot,usr/portage,home}
# mount /dev/sda1 /mnt/funtoo/boot
# mount /dev/sda5 /mnt/funtoo/usr/portage
# mount /dev/sda6 /mnt/funtoo/home
The install -d command just creats all the needed folders for later mountpoints for us. If you like you can control it by using ls /mnt/funtoo after the install -d part. Now you are ready to install your base system, read on in Downloading the System.
GPT unencrypted
That part is really similiar to the unencrypted MBR, but see for yourself:
# swapon /dev/sda3
# mount /dev/sda4 /mnt/funtoo
# install -d /mnt/funtoo/{boot,usr/portage,home}
# mount /dev/sda1 /mnt/funtoo/boot
# mount /dev/sda5 /mnt/funtoo/usr/portage
# mount /dev/sda6 /mnt/funtoo/home
MBR/GPT encrypted
Now mount the system so we can setup the system in the next step.
# swapon /dev/mapper/vg-swap
# mount /dev/mapper/vg-root /mnt/funtoo
# install -d /mnt/funtoo/{boot,usr/portage,home}
# mount /dev/sda1 /mnt/funtoo/boot
# mount /dev/mapper/vg-portage /mnt/funtoo/usr/portage
# mount /dev/mapper/vg-home /mnt/funtoo/home
Downloading the System
The next step is to download the base system and portage tree and set up both. Here a list of packages we have:
| Arch (32/64 bit) | Processors | Stable Release | Current Release |
|---|---|---|---|
| 64-bit Install Images for PC-compatible processors | |||
| 64 | Generic Intel and Amd 64-bit Processors | generic_64 | generic_64 |
| 64 | Intel Core2 Series and most Atom Processors | core2_64 | core2_64 |
| 64 | Intel Core i3, i5, i7 | N/A | corei7 |
| 64 | AMD Athlon 64 and Opteron Processors (K8 Family or higher) | amd64-k8 | amd64-k8 |
| 32-bit Install Images for PC-compatible processors | |||
| 32 | Intel Core2 Series, i3, i5, i7 and Atom Processors | N/A | core2_32 |
| 32 | N/A | amd64-k8_32 | |
| 32 | Generic x86 processors (intel80486+) | i486 | i486 |
| 32 | Generic P6-class (Pentium Pro/Pentium II compatible) | i686 | i686 |
| 32 | Athlon XP and Athlon 64-based CPU (32-bit mode) | N/A | athlon-xp |
| 32 | Intel Pentium 4 Processors | N/A | pentium4 |
| OpenVZ Templates for PC-Compatible Systems | |||
| 32 | 32-bit OpenVZ Images | OpenVZ x86-32bit | OpenVZ x86-64bit |
| 64 | 64-bit OpenVZ Images | OpenVZ x86-64bit | OpenVZ x86-64bit |
| SPARC processor Images | |||
| 32/64 | Generic SPARC v9 processors (use this one if the ultrasparc I/II stages are inadequate for you) | N/A | sparc_v9 |
| 32/64 | UltraSPARC I & UltraSPARC II series (choose this one in doubt) | N/A | ultrasparc |
| 32/64 | UltraSPARC III and UltraSPARC IV series | N/A | ultrasparc3 |
| 32/64 | Niagara (UltraSPARC T1) | N/A | niagara |
| 32/64 | Niagara 2 (UltraSPARC T2/ UltraSPARC T2+) | N/A | niagara2 |
If you found your desired image above, just change to /mnt/funtoo and download the stage3 and portage-tree images.
# cd /mnt/funtoo # elinks http://ftp.osuosl.org/pub/funtoo/funtoo-current/x86-64bit/generic_64/
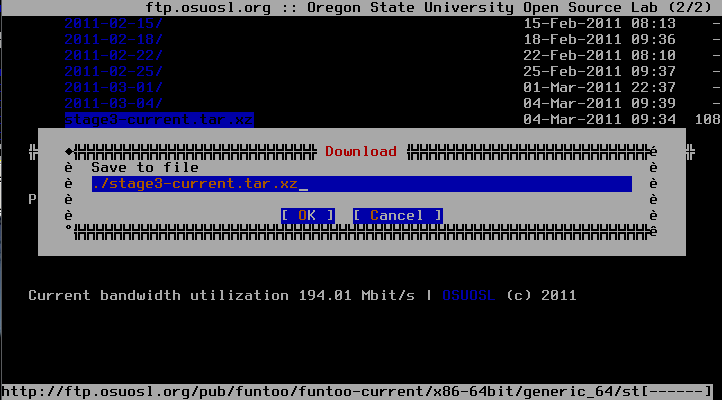
this shows you the site presented and by going down with the arrow keys to stage3-latest.tar.xz until it is highlighted you can download it by pressing D. Then move up in the directory structure (..-link) and go to the snapshot directory or quit elinks after downloading finished and start it again with like that
# elinks http://ftp.osuosl.org/pub/funtoo/funtoo-current/snapshots/
here you will now download the portage tree (portage-latest.tar.xz). The Download dialog will look in both cases like that:(Note outdated image, 'stage3-current.tar.xz' is now 'stage3-latest.tar.xz')
When both downloads have finished quit elinks by typing q. The downloaded files should be located in /mnt/funtoo. Now that this is done, let us move on to installing your base system.
Installing the base system
Now that we have the base system and the portage tree downloaded, we will install it. First install the stage3. it is really easy.
# tar xfvpJ stage3-latest.tar.xz
That will output many lines, and return a command-prompt line when finished.
Next we need to extract the funtoo-portage-tree. For that we need to change to the future /usr dir, and extract there the portage.
# cd /mnt/funtoo/usr # tar xfvpJ ../portage-latest.tar.xz
This time there will be no output, but when the unpacking has finished, the result will be an empty command prompt. We still need to checkout the tree, but this can only be done from inside the chroot environment.
At this state of the setup we have setup most of our system. If you choose to use the fast genkernel method later on, the hardest part is already done. If you choose to manually configure the kernel, you still have quite a bit work ahead of you.
Chrooting
Before we can finally chroot into your system, there are a couple of things that need to be done before, like mounting the proc and dev filesystem.
# mount -t proc none /mnt/funtoo/proc # mount --bind /dev /mnt/funtoo/dev
to have a working network inside of your chrooted system later you need to copy the resolv.conf file too:
# cp -L /etc/resolv.conf /mnt/funtoo/etc
Now we can chroot into your Funtoo system
# env -i HOME=/root TERM=$TERM SHELL=/bin/bash # chroot /mnt/funtoo /bin/bash
Now that we are inside your new system, you'll need to update your environment, use the following commands to do so:
# source /etc/profile # env-update
We also recommend you to change the default command prompt while you are inside the chroot, as it will avoid confusions if you have to change terminals for anything. To do so use the following command:
# export PS1="(chroot) $PS1"
Congratulations! You are now inside your new Funtoo Linux operating system.
Updating the Portage tree
As we have installed the Portage snapshot during the installation, we now need to "activate" the Portage tree by selecting the funtoo.org branch.
By default, the master branch is enabled, which saves space when storing the tree inside a tarball, but that branch only contains a README with the same instructions as the ones given here.
To activate the funtoo.org branch, do the following:
# cd /usr/portage/ # git checkout funtoo.org Checking out files: 100% (85007/85007), done. Switched to branch "funtoo.org"
You'll now be able to see thousands of glorious ebuilds inside your Portage tree :)
After activating the funtoo.org branch you need to sync your tree to the newest glorious funtoo ebuilds. Run:
# emerge --sync
This will now update the tree to the current state, which normally changes twice a day.
Setting the default options
Like any other Linux Distribution, Funtoo Linux has it's share of configuration files, that need to be edited by you. The following table gives you an overview of these files and for what they are there:
| File | Description |
|---|---|
| /etc/portage/make.conf | Parameters used by gcc compiler |
| /etc/fstab | Device to mountpoint definitions |
| /etc/conf.d/hostname | Setting your hostname |
| /etc/rc.conf | OpenRC configuration file. |
| /etc/conf.d/keymaps | Keyboard configuration file. |
| /etc/conf.d/hwclock | System clock to use. |
| /etc/conf.d/consolefont | Fonts to be used in console display. This doesn't affect GUI terminal emulators. |
| /etc/env.d/99editor | Default editor. |
| /etc/localtime | Your timezone. |
| /etc/make.profile | Type of installation (desktop, server...). |
| /etc/conf.d/modules | Kernel modules to load |
| /etc/locale.gen | Localization. |
| /etc/env.d/02locales | Localization for old programs. |
If you are installing an english Funtoo, you are lucky, as you won't need to edit many of the files above, if not, don't be afraid, we will walk through the configuration of these files in the following together.
First we will get a mighty editor with great syntax highlighting as it is not provided in our main system we will merge it, if you don't like to please replace in the following edit sections the part vim <path/filename> with your editor <path/filename> where editor is replaced by vi or nano -w.
First let us get vim so we have the perfect highlighting from it for our personal help.
# emerge -avt vim
that will result in an output like that
just accept the output with Enter and it will install vim for you, while you wait for vim to get emerged, here are the some basic usage instructions for ViM. ViM has a multimode interface, if you start it, it is in Command mode, the second mode is the Edit mode which you will enter from the Command mode by pressing i, to go back into the Command mode press ESC. After you have edited a config file, you want to save it, for that you have to be in Command mode and then simple press :w<ENTER>, it will save the file, a closing is done with :q<ENTER>, if you changed content in the file that shouldn't be saved use :q! and for saving and closing the file :wq, thats all, the visual mode is in that context not very useful, so we leave it out. Now that you know the basic usage of ViM and it has emerged we will now start configuring the config files.
/etc/portage/make.conf
First open that file
# vim /etc/portage/make.conf
This file contains something similar to the following. You may or may not have a CFLAGS variable set already depending on what stage 3 tarball you used:
ACCEPT_KEYWORDS="~amd64" SYNC="git://github.com/funtoo/portage-mini-2010.git" CHOST="x86_64-pc-linux-gnu"
In ACCEPT_KEYWORDS, ~amd64 is used for current 64-bit builds; There is no tilde for the stable build. The default value is (~)x86 for 32 bit. The ACCEPT_KEYWORDS line should not be altered. Keep it as supplied in the default file. It is also important to not change the CHOST line.
CFLAGS
If you're only building packages for your host processor and not any others then the recommended CFLAGS setting is:
CFLAGS="-march=native -O2 -pipe"
If you want to use the parameter for your processor exclusively (Core2 in this case, see http://www.funtoo.org/Core2_64), you could use...
CFLAGS="-march=core2 -O2 -pipe"
See https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/x86-Options.html#x86-Options
Since gcc-4.2, -mtune=native and -march=native will produce code optimized for the host processor. -mtune=native has no effect if GCC does not recognize the processor. More information can be found in the GCC online docs. <-- link broken.
The value native selects the best architecture option for the host processor, so this should not be used if you intend to compile packages for a different CPU.
CXXFLAGS
Normally, this flag is set to the same values as CFLAGS:
CXXFLAGS="${CFLAGS}"
MAKEOPTS
With MAKEOPTS you define how many parallel compilations should occur when you compile a package. A good choice is the number of CPUs (or CPU threads) in your system plus one (Note: this guideline isn't always perfect). If for example you have a dual core processor without hyperthreading, then you would set MAKEOPTS to 3:
MAKEOPTS="-j3"
If you're unsure of how many processors/threads you have, then use /proc/cpuinfo to help you.
# cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep "model name" | wc -l 16
Set MAKEOPTS to this number plus one:
MAKEOPTS="-j17"
USE
USE flags define what functionality is enabled when ebuilds are built. It is not recommended to add a lot of them during installation. You should wait until you have a working, bootable system to do so. The following USE flags are a recommended starting point for new systems:
USE="-gnome -gtk -kde -kdeenablefinal -ldap nls -qt3 -qt3support -qt4 userlocales"
The minus(-) sign tells gcc not to use the flag when compiling. USE flags gnome, gtk, kde, qt3, qt3support, and qt4 will be set later if you install a desktop envrionment.
A Funtoo guide to USE flags will be available in the future. For now, you can find out more information about USE flags in the Gentoo Handbook.
GENTOO_MIRRORS
This is the mirror from which emerge gets a lot of the source files. It is usually not necessary to set this flag. In the following ewxample, the Waterloo University is used (a fast and reliable Canadian mirror). Please set this variable to a mirror local to your country.
GENTOO_MIRRORS="ftp://mirror.csclub.uwaterloo.ca/gentoo-distfiles/ http://distfiles.gentoo.org"
LINGUAS
LINGUAS tells Portage which local language to compile the system and applications in (those who use LINGUAS variable like OpenOffice). It is not usually necessary to set this if you use English. Otherwise, if you want another language, replace fr (French) for the code of your mother language, e.g. de for German.
LINGUAS="fr"
or for multiple language support you might also use:
LINGUAS="en de fr"
/etc/portage/make.conf example
You should find an example file at /etc/portage/make.conf.example.
An example of a /etc/portage/make.conf file could look like that:
# These settings were set by the metro build script that automatically built this stage.
# Please consult /etc/make.conf.example for a more detailed example.
ACCEPT_KEYWORDS="x86"
FEATURES="mini-manifest"
SYNC="git://github.com/funtoo/portage-mini-2010.git"
CHOST="i686-pc-linux-gnu"
CFLAGS="-march=i686 -O2 -pipe"
CXXFLAGS="${CFLAGS}"
MAKEOPTS="-j2"
USE="-gnome -gtk -kde -kdeenablefinal -ldap nls -qt3 -qt3support -qt4 userlocales"
GENTOO_MIRRORS="ftp://mirror.csclub.uwaterloo.ca/gentoo-distfiles/ http://distfiles.gentoo.org"
LINGUAS="fr"
INPUT_DEVICES="evdev synaptics"
VIDEO_CARDS="vesa radeon"
PORT_LOGDIR="/var/log/portage"
PORTAGE_ELOG_CLASSES="log warn error info"
PORTAGE_ELOG_SYSTEM="echo:log,warn save:log,warn,error,info syslog:error"
/etc/fstab
This file is used for the configuration of the mountpoints for the system. As we have two different setups described above, here are the two examples for these.
# vim /etc/fstab
unencrypted MBR
# The root filesystem should have a pass number of either 0 or 1. # All other filesystems should have a pass number of 0 or greater than 1. # # NOTE: If your BOOT partition is ReiserFS, add the notail option to opts. # # See the manpage fstab(5) for more information. # # <fs> <mountpoint> <type> <opts> <dump/pass> /dev/sda1 /boot ext2 noauto,noatime 1 2 /dev/sda2 none swap sw 0 0 /dev/sda3 / ext4 noatime 0 1 /dev/sda5 /usr/portage ext4 noatime 0 1 /dev/sda6 /home xfs defaults,noatime 0 1 #/dev/cdrom /mnt/cdrom auto noauto,ro 0 0 none /dev/shm tmpfs nodev,nosuid,noexec 0 0
unencrypted GPT
# The root filesystem should have a pass number of either 0 or 1. # All other filesystems should have a pass number of 0 or greater than 1. # # NOTE: If your BOOT partition is ReiserFS, add the notail option to opts. # # See the manpage fstab(5) for more information. # # <fs> <mountpoint> <type> <opts> <dump/pass> /dev/sda1 /boot ext2 noauto,noatime 1 2 /dev/sda3 none swap sw 0 0 /dev/sda4 / ext4 noatime 0 1 /dev/sda5 /usr/portage ext4 noatime 0 1 /dev/sda6 /home xfs defaults,noatime 0 1 #/dev/cdrom /mnt/cdrom auto noauto,ro 0 0 none /dev/shm tmpfs nodev,nosuid,noexec 0 0
encrypted
That time the setup is the same for both MBR and GPT partition layout:
# The root filesystem should have a pass number of either 0 or 1. # All other filesystems should have a pass number of 0 or greater than 1. # # NOTE: If your BOOT partition is ReiserFS, add the notail option to opts. # # See the manpage fstab(5) for more information. # # <fs> <mountpoint> <type> <opts> <dump/pass> /dev/sda1 /boot ext2 noauto,noatime 1 2 /dev/mapper/vg-swap none swap sw 0 0 /dev/mapper/vg-root / ext4 noatime 0 1 /dev/mapper/vg-portage /usr/portage ext4 noatime 0 1 /dev/mapper/vg-home /home xfs defaults,noatime 0 1 #/dev/cdrom /mnt/cdrom auto noauto,ro 0 0 none /dev/shm tmpfs nodev,nosuid,noexec 0 0
/etc/conf.d/hostname
Here you will set up your hostname for the PC. So choose a name for your PC and set it up in that file:
# vim /etc/conf.d/hostname # Set to the hostname of this machine hostname="<your-hostname>"
/etc/rc.conf
You may use this file as-is. However, it is a good idea to set rc_logger to yes. That will create a log file which is handy when problems are encountered with OpenRC scripts. Very helpful for fixing things.
Another good option here is the rc_interactive flag, if you are playing around with a new graphical display manager or aren't that used with the upgrade procedure of the graphical environement. if rc_interactive is set to yes, you will be able to interactively manipulate the boot process, what means you can decide what you want to start or not, like the graphical environment for example.
Other options have really good explainations inside of the /etc/rc.conf file.
/etc/conf.d/keymaps
You do not have to alter that file if you have a US English keyboard. Otherwise, edit file and set keymap to your keyboard model. For example, cf for French Canadian keyboard, fr for French Azerty and de for German Qwertz.
/etc/conf.d/hwclock
If you dual boot with Windows, you'll need to edit this file and change clock to local. Otherwise you should not normally need to edit this file.
You should define your timezone in /etc/timezone:
# vim /etc/timezone Europe/Berlin
anoteher value might be
America/Denver
so you might get an idea how it should look like, if not have a look at /usr/share/zoneinfo it will give you the entry after the path like /usr/share/zoneinfo/<Content of /etc/timezone> like for Germany you will find a path in there that looks like /usr/share/zoneinfo/Europe/Berlin.
/etc/conf.d/consolefont
There is nothing to edit in that file.
/etc/env.d/99editor
Create and edit that file to instruct your system about the default editor it should use.
vim /etc/env.d/99editor
Type in :
EDITOR="/usr/bin/vim"
Replace the above line with the editor of your choice, if you had been happy so far with ViM just paste it in as is, if not use nano, vi or what else you like.
/etc/localtime
If you came here from Gentoo, it was advised to copy the file from the zoneinfo dir to here. We advise you to create a symbolic link from the zoneinfo dir to /etc/localtime. As in the hwclock section above, we need your timezone parted in LAND/TOWN like for Germany Europe/Berlin. Now, create the symbolic link. More info about it can be found in the /usr/share/zoneinfo dir.
ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/Europe/Berlin /etc/localtime
That command sets the timezone to Central European Time.
/etc/make.profile
Here you select which type of environment you want the gcc-compiler to take into account. That will dress up an environment with a list of pre-defined USE flags.
To list all available profiles run:
eselect profile list
The output will look like that:
[1] default/linux/x86/2008.0 * [2] default/linux/x86/2008.0/desktop [3] default/linux/x86/2008.0/developer [4] default/linux/x86/2008.0/server
Profile defaults to 2008.0 (See the star). To create a profile for DE (Desktop Environment) run:
eselect profile set 2
Funtoo only supports the 2008.0 profile and the 2008.0 profile children. Use one of these profiles until 'funtoo-1.0' is ready.
/etc/conf.d/modules
With Funtoo, OpenRC loads modules from /etc/conf.d/modules using the line:
modules_2_6="list of modules"
With Funtoo, define module arguments as follows:
module_module-name_args_2_6="module arg=value"
Localization
/etc/locale.gen and /etc/env.d/02locales are used to support your local language. The last one is required just in case there still are old programs installed.
You do not need to amend anything if your locales are US English. The following are examples for German. You can look in /usr/share/i18n/SUPPORTED for the default list of supported combinations or look in /usr/share/i18n/locales to determine values to use.
# vim /etc/locale.gen
Put this value into the file for German support:
de_DE.UTF-8 UTF-8
for a multiple language support it might look like that:
de_DE.UTF-8 UTF-8 fr_CA.UTF-8 UTF-8 en_US.UTF-8 UTF-8
Edit /etc/env.d/02locales according to that layout:
# vim /etc/env.d/02locales
and put in these lines:
LANG="de_DE.UTF-8" LANGUAGE="de_DE.UTF-8"
Finally after we editet all the localization files generate the localized environment:
locale-gen && source /etc/profile
Kernel
Now that you have the base system running, you need to install a kernel. If you decided to use a standard setup with an unencrypted GPT disc layout or the old unencrypted MBR disc layout, a fast solution would be to use the genkernel solution. If you used the standard setup with an encrypted GPT disc layout or the old encrypted MBR disc layout, you have to use the manual kernel steps.
choosing a kernel
First, you need to choose a kernel version you would like to install on your system. The following table will give you an overview of which kernels are available and who should use them.
| Kernel ebuild | Description | masked | Prefered Users | eselect kernel set |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sys-kernel/* | generates symlink | |||
| cell-sources | Full sources including the cell/ps3 patchset for the 2.6 kernel tree | [ Masked ] | unsure | |
| ck-sources | Con Kolivas' high performance patchset + Gentoo patchset sources | unsure | ||
| debian-sources | Debian Sources - with optional OpenVZ support | NO | ||
| gentoo-sources | Full sources including the Gentoo patchset for the 2.6 kernel tree | default for most users | YES | |
| git-sources | The very latest -git version of the Linux kernel | for the versed user | YES | |
| hardened-sources | Hardened kernel sources (kernel series 2.6) | not supported atm | YES | |
| mips-sources | Linux-Mips GIT sources for MIPS-based machines, dated 20110207 | [ Masked ] | unsure | |
| mm-sources | Andrew Morton's kernel, mostly fixes for 2.6 vanilla, some vm stuff too | unsure | ||
| openvz-sources | Full sources including OpenVZ patchset for the 2.6.18 kernel tree | For users that want to build a OpenVZ server | unsure | |
| pf-sources | Linux kernel fork with new features, including the -ck patchset (BFS), BFQ, TuxOnIce and LinuxIMQ | unsure | ||
| rhel5-openvz-binaries | RHEL5 kernel with OpenVZ patchset - initrd and bzImage | YES | ||
| rhel5-openvz-sources | Full Linux kernel sources - RHEL5 kernel with OpenVZ patchset | unsure | ||
| rhel6-openvz-binaries | RHEL6 kernel with OpenVZ patchset - initrd and bzImage | unsure | ||
| rhel6-openvz-sources | Full Linux kernel sources - RHEL5 kernel with OpenVZ patchset | unsure | ||
| sparc-sources | Full sources for the Gentoo Sparc Linux kernel | [ Masked ] | YES | |
| sysrescue-std-binaries | System Rescue CD Full sources for the Linux kernel, including gentoo and sysresccd patches - initrd and bzImage | [ Masked ] | unsure | |
| sysrescue-std-sources | System Rescue CD Full sources for the Linux kernel, including gentoo and sysresccd patches. | unsure | ||
| tuxonice-sources | TuxOnIce + Gentoo patchset sources | unsure | ||
| usermode-sources | Full sources for the User Mode Linux kernel | [ Masked ] | unsure | |
| vanilla-sources | Full sources for the Linux kernel | YES | ||
| vserver-sources | Full sources including Gentoo and Linux-VServer patchsets for the 2.6 kernel tree. | unsure | ||
| xbox-sources | Full sources for the Xbox Linux kernel | [ Masked ] | unsure | |
| xen-sources | Full sources for a dom0/domU Linux kernel to run under Xen | unsure | ||
| zen-sources | The Zen Kernel Sources v2.6 | unsure |
For the next section, we will assume that you selected gentoo-sources for your kernel setup. If not, please replace gentoo-sources in the next section with your selection. If you are unsure, please follow our suggestion to use the gentoo-sources.
genkernel
That part would be fast done in general, we will now guide you through that process. First, we need to install the needed tools for it. So, let's do it!
# emerge -avt genkernel gentoo-sources Calculating dependencies... done! These are the packages that would be merged, in reverse order: [ebuild N ] sys-kernel/gentoo-sources-2.6.38-r4 USE="-build -deblob -symlink" 134 kB [ebuild N ] sys-kernel/genkernel-3.4.12.6-r2 USE="-bash-completion (-ibm) (-selinux)" 11,556 kB Total: 2 packages (2 new), Size of downloads: 11,690 kB Would you like to merge these packages? [Yes/No]
After answering the above question with "Yes", it will download and install the packages for you. Next, you need to set the symlink from /usr/src/linux to the /usr/src/linux-version directory. There are two ways to do so. If you have selected a version that is supported by eselect, it would be really simple for you, just do:
# eselect kernel list # eselect kernel set 1
The first command should list the kernel you have selected. If that isn't the case, the second command to set this kernel version isn't needed, else the second one sets the symlink automatically for you. As eselect kernel command will scan your /usr/src directory, it should list every kernel-sources listed above, if that isn't the case, please report the failing to the funtoo-dev mailing list, Funtoo Forums or contact us directly in IRC at #funtoo. As a workaround you could use the following steps to make your kernel-sources usable:
# cd /usr/src # rm linux # ls linux-sources # ln -s linux-sources linux
where linux-sources is the directory that the ls command above showed you.
When you finished the selection of your kernel you will now bake your first kernel, using the genkernel or fast way. Execute for that the following command:
# genkernel --menuconfig all
if you have a special config predefined use
# genkernel --kernel-config=config-name --menuconfig all
else if you have choosen an encrypted setup, use the following command to include all the tools you need for bootup:
# genkernel --lvm --luks --menuconfig all
the above used options are doing the following:
- --kernel-config: use the given name located in the kernel source tree (/usr/src/linux by default is taken unless overridden by --kerndir)
- all: rebuild the kernel image and the initramfs ramdisk image (aside of kernel modules, the ramdisk image contains tools such as BusyBox and some generic startup scripts, depending on options you use on the command line several additional tools like lvm or raid volume management can be incorporated as well).
- --lvm: Includes support for storage using via Logical Volume Management (LVM2) from static binaries, if available to the system. Relevant (static) LVM2 binaries are compiled if they are unavailable. Be sure to install the lvm2 package on your system with emerge lvm2 before enabling this flag.
- --luks: Includes support for Linux Unified Key Setup or LUKS. This will allow you to use a device encrypted by LUKS which contains the root filesystem. On the bootloader, you then set that encrypted device as the value of crypt_root (and real_root shall be the unencrypted device LUKS creates).
- --menuconfig: lets you set options for kernel compile manual
The --menuoption will present you the following screen:
default options for unencrypted/encrypted setup
We advised you above to use a partitioning scheme based on the following file system types:
- ext2
- swap
- ext4
- xfs
You now need to activate all of them so you can boot your system later, these options can be found at:
Under File systems:
<*> Second extended fs support <*> The Extended 4 (ext4) filesystem [*] Ext4 extended attributes (NEW) [ ] Ext4 POSIX Access Control Lists (NEW) [ ] Ext4 Security Labels (NEW) [ ] EXT4 debugging support (NEW) <*> XFS filesystem support [ ] XFS Quota support (NEW) [ ] XFS POSIX ACL support (NEW) [*] XFS Realtime subvolume support [ ] XFS Debugging support (EXPERIMENTAL) (NEW)
If you furthermore decided to follow our advice and to use a GPT-Partitioning scheme, which will be your default, you will need to activate it in your kernel by using the following options:
Under File systems-->Partition Types:
[*] Advanced Partition Selection (PARTITION_ADVANCED) [*] EFI GUID Partition Support (EFI_PARTITION)
additional encrypted options
It is very important to add the following parts in your kernel setup, when you used the above GPT or MBR encrypted setup. Under
Under General setup:
[*] Initial RAM filesystem and RAM disk (initramfs/initrd) support
and Under Device Drivers:
[*] Multiple devices driver support <*> Device Mapper Support <*> Crypt target support
and finally Under Cryptographic API:
<*> XTS support (EXPERIMENTAL) -*- AES cipher algorithms
Finally exit the menuconfig for your kernel and get a coffee. You have done a good bit of work so far... :)
manual kernel
You can use genkernel to automatically compile your kernel, but this tends to create a bloated kernel, compatible with just about any computer, anyplace, any time. On the other hand, you can manually configure and compile your kernel, to give you complete control, for the smallest and fastest kernel(s) that you can build for your specific computer. However, manual kernel configuration is often called by many users, the hardest step in installing Funtoo. But it is also very worth learning how to do it. Be warned that it make take several reconfigurations, compiles and reboots, until you have a working system. Plus, for the encrypted hdd version, you will have to do a bit more work than above, but if you have gotten this far, you should be able to handle it.
install and config
First you will have to install the kernel image you selected above. In the following we again use the kernel we think might be the default choice of you, gentoo-sources, but you can feel free to replace it with any of the above ones. So now install your kernel-sources:
# emerge -avt gentoo-sources
After answering the above question with Yes, emerge will download and install the kernel-sources for you. Next you need to set the symlink from /usr/src/linux to the /usr/src/linux-version directory. There are two ways to do so, the default way would be to use the following command sequence:
# eselect kernel list # eselect kernel set 1
The first command will list the kernel or kernels for which you have used emerge to install the corresponding source code packages. The character * is used to indicate the currently selected default kernel package. In other words, the command eselect kernel list will scan and list directories in your /usr/src directory , each named after a different kernel source code. It will then show with a * the directory currently pointed to by the /usr/src/linux link. The second command is not needed, as long as the correct kernel source has been selected. Otherwise, use this command and the number of the corresponding kernel directory, to set your /usr/src/linux link.
If the eselect kernel command does not work correctly, please report the failing to the funtoo-dev mailing list, Funtoo Forums or contact us directly in IRC at #funtoo.
As a workaround or for educational purposes, you could use the following equivalent commands. For example, to make gentoo-sources available for compiling your kernel, enter:
# cd /usr/src # rm linux # ls gentoo-sources-3.5.4 # ln -s gentoo-sources-3.5.4 linux
where gentoo-sources is the directory that the ls command above showed you.
Now you are nearly ready to configure your kernel. First switch to a second terminal with Alt+F2 and execute lspci and copy the output, most importantly the names of the VGA, Ethernet and Network devices currently in your system. Knowing these device names will be needed if you need help for default options at the Debian GNU/Linux device driver check page. Some options there aren't in your kernel or may have other names but it is a good source for getting default options help for devices.
Now move back to your chrooted system (Alt+F1) and start the configure process with
# cd /usr/src/linux # make menuconfig
This will present you a screen similar to the following:
start setting the options you know about or the ones the page above gave you. You need to at least set the following options:
Here are some more sources you may like to read for configuring your kernel the old fashioned manual way:
- http://kernel-seeds.org
- http://swift.siphos.be/linux_sea/ch07.html
- http://www.gentoo.org/doc/en/kernel-config.xml
default options for unencrypted/encrypted setup
We advised above to use a partitioning scheme based on the following filesystemtypes:
- ext2
- swap
- ext4
- xfs
You now need to activate all of them so you can boot your system later, these options can be fount at:
If you furthermore decided to follow our advice and use a GPT-Partitioning scheme, what will be our default, you need to activate it in your kernel by using the following options:
additional encrypted options
It is very important to add the following parts in your kernel setup, when you used the above GPT or MBR encrypted setup. Under
and under
and finaly under
building the kernel the manual way
Now that all the options are set exit menuconfig and answer the question about saving your config with YES. That already was the hardest part, now bake your kernel.
# make # make modules_install # cp arch/<architecture>/boot/bzImage /boot/bzImage-<versionnumber>
This code-sequence will need to be explained, the first command make will bake your kernel, it will take some time, so feel free to get a coffee. :) if you don't have one available here is one from us |_|). make modules_install generates the modules for the kernel and builds them, the third command in the sequence needs to be adjusted by you, if you use a 32bit system replace <architecture> with x86 and for 64bit systems with x86_64, finally replace the <versionnumber>-string with a for you readable and unique versionnumber like 2.6.38-rc7-mykernel-v1 or something like that, then the command copies over your baked kernel to /boot and you are ready to get to the next step....
Bootloader
boot-update
boot-update is the default boot-loader configuration tool in funtoo. You need to install it with
# emerge -avt boot-update
This will install boot-update and grub2 for you. Next you need to configure it. That is done in /etc/boot.conf:
# vim /etc/boot.conf
/etc/boot.conf will look somewhat like the following:
boot {
generate grub
default "Funtoo Linux 64-bit"
timeout 10
}
display {
gfxmode 1440x900
#background /boot/
}
color {
normal cyan/black
highlight black/cyan
}
default {
scan /boot
kernel bzImage[-v] kernel[-v] vmlinuz[-v]
initrd initramfs[-v]
# root=auto will cause the parameter
# from your /etc/fstab. rootfstype=
params video=vesafb root=auto rootfstype=auto
# an alternate graphics mode can be set
# default is inherited from display:
# gfxmode 1024x768
}
"altboot" {
params += init=/bin/bash
}
"Funtoo Linux 64-bit gpt" {
kernel bzImage[-v]
}
"Funtoo Linux genkernel" {
kernel kernel[-v]
initrd initramfs[-v]
params += real_root=auto
}
"Funtoo Linux 64-bit encrypted gpt/mbr manual kernel" {
kernel bzImage[-v]
initrd /initramfs.cpio.gz
params += enc_root=/dev/sda3 lvm luks root=/dev/mapper/vg-root rootfstype=ext4 resume=swap:/dev/mapper/vg-swap quiet
}
If you decided to do a manual kernel, with an encrypted HDD, you will need to read the next section after you made the changes to your config. If you decided to use genkernel or a manual kernel with unencrypted HDD, all is OK and it is now safe for you to go to the Grub2 setup.
encrypted disk with manual kernel
As you decided to make an encrypted disk setup with a manual kernel, you need to instal slashbeast's better-initrmafs. It is very simple to do. First clone the git-repository. If you aren't confident with git, feel free to have a look at our Git Guide.
# install -d /root/.git # cd /root/.git # git clone git://github.com/slashbeast/better-initramfs.git # cd better-initramfs # git checkout v0.3 # less README.rst # echo "sys-apps/busybox static" >> /etc/portage/package.use/busybox && echo "sys-fs/cryptsetup static" >> /etc/portage/package.use/cryptsetup && echo "sys-fs/lvm2 static" >> /etc/portage/package.use/lvm2 # emerge -avt busybox cryptsetup lvm2 # make >>> New better-initramfs is not backward compatible, read ChangeLog file. >>> Preparing binary files... >>> Adding /bin/busybox... >>> Adding /sbin/cryptsetup... >>> Adding /sbin/lvm.static... >>> Building image... >>> initramfs.cpio.gz is ready. # cp initramfs.cpio.gz /boot
Now you are ready to setup grub2. Just go to the next section.
= Updating better-initramfs =
As the better-initrmafs project isn't controlled at the moment by an ebuild, you will need to take care of updating it by yourself, but it is very easy to do so:
# git checkout master # git pull # less ChangeLog # git checkout vx.x # make
where x.x is a version announced in the ChangeLog. At the moment the stable is 0.3.
setting up grub2
This step is easy. It is done with two commands;
# grub-install --no-floppy /dev/sda # boot-update
A successful run of boot-update might will look like this:
boot-update 1.5.2 / Copyright 2009-2011 Funtoo Technologies
[use option "-l" for license info, "-h" for help]
* Generating config for grub...
DEFAULT > Funtoo Linux 64-bit - bzImage-2.6.39-rc7-git-a2b9c1f
Funtoo Linux 64-bit - bzImage-2.6.39-rc7-git-446cc63
Funtoo Linux 64-bit - bzImage-2.6.39-rc7-git-df8d06a
* WARN : multiple matches found for default "Funtoo Linux 64-bit" - most recent used.
* Completed successfully with warnings.
Extlinux
For Extlinux you will find a guide for setup at Extlinux.
finalize Setup
Necessary System Tools
As some tools are providing the same functionality, it is up to you to choose which ones you like to use. The next sections are giving you an overview of tools you might like to use and install, but all are optional.
System Logger
Linux and Unix have an excellent history of logging capabilities, if you want you can log from only special stuff up to everything that happens on your system in logfiles, for that behavior is a system logger the reason.
There are several in our repository from which you can choose:
- sysklogd, which is a traditional set of system logging daemons,
- syslog-ng, which is an advanced system logger and
- metalog, which is a highly-configurable system logger,
- rsyslog, seems to be a popular choice, default syslog of Fedora, RHEL, openSUSE, Debian and Ubuntu
- there might be others available too, but at the moment we aren't aware of them.
We advice you to install next to sysklogd or syslog-ng the logrotate tool, as those system loggers don't provide a rotation machanism for the log files.
Just install the desired one like the example shows:
# emerge syslog-ng # rc-update add syslog-ng default
Optional: Cron Daemon
Although this is optional it is in our opinion very handy and wise to install one. But you might ask yourself now "What the hell is a cron daemon?" A cron daemon just executes scheduled commands, so you see it can be very handy if you need to execute commands regularly.
In our tree there are three possible cron daemons; dcron, fcron and vixie-cron. We would like to advise you to use fcron, but it depends on what you like. also vixie-cron might be easier, as you don't need to execute crontab /etc/crontab, fcron might be more powerful.
# emerge fcron # rc-update add fcron default # crontab /etc/crontab
Optional: File Indexing
If you like to index your files for a fast search, you need to install mlocate so you can use the locate command to quickly search for them:
# emerge mlocate # updatedb
File System Tools ==
As we used some special filesystems above you need to at least install xfsprogs, but there might be some others too, the following table gives you an overview:
| File System | Tool | install command | needed |
|---|---|---|---|
| XFS | xfsprogs | emerge xfsprogs | X |
| JFS | jfsprogs | emerge jfsprogs | |
| reiserfs | reiserfsprogs | emerge reiserfsprogs | |
| btrfs | btrfs-progs | emerge btrfs-progs |
Networkconfig
The Easy (Dynamic) Way
When configuring your network, one option is to skip traditional network configuration and simply rely on DHCP. This is by far the simplest method of configuring your network. If you are on a wired network, no other steps are typically required beyond enabling a DHCP client, and Funtoo Linux includes dhcpcd 5.x by default. To enable DHCP at system startup, you would add dhcpcd to your default runlevel as follows:
# rc-update add dhcpcd default
If your going to use a third party package such as Network Manager or Wicd to manage your network then do not add dhcpcd to any runlevel. These packages handle DHCP for you.
The Modular Way
DHCP isn't always an option, and for these situations, Funtoo Linux offers its own modular, template-based network configuration system. This system offers a lot of flexibility for configuring network interfaces, essentially serving as a "network interface construction kit." This system can be used by itself, or even combined with dhcpcd -- if you limit dhcpcd to only manage certain network interfaces.
Here are the key components of the template-based network configuration system:
/etc/init.d/netif.lo -- An init script that configures the localhost interface.
/etc/netif.d -- This is a directory that contains various network configuration templates. Each of these templates is focused on configuring a particular type of network interface, such as a general static IP-based interface, a bridge interface, a bond interface, etc.
/etc/init.d/netif.tmpl -- This is the master init script for the template-based network configuration system. New interfaces are added to your system by creating symbolic links to this file in /etc/init.d.
So, if you wanted to use this system to configure eth0 with a static IP address, you would create a netif.eth0 symlink to netif.tmpl as follows:
# cd /etc/init.d # ln -s netif.tmpl netif.eth0
Then, you would create an /etc/conf.d/netif.eth0 configuration file that would specify which template to use from the /etc/netif.d directory:
template="interface" ipaddr="10.0.1.200/24" gateway="10.0.1.1" nameservers="10.0.1.1 10.0.1.2" domain="funtoo.org"
To complete our static IP network configuration we would need to:
# rc-update add netif.eth0 default
When configuring your own static network interface, one of ipaddr or ipaddrs is required and should specify the IP address(es) to configure for this interface, in "a.b.c.d/netmask" format. Optional parameters include gateway, which defines a default gateway for your entire network, and if set should specify the gateway's IP address. In addition, domain and nameservers (space-separated if more than one) can be used to specify DNS information for this interface.
Configuration Variables
Interface Variables
The following variables are supported by the interface and bridge templates:
- ipaddr or ipaddrs: specify IPv4 or IPv6 address(es) for the interface. IP addresses should be specified in "IP/netmask" format, such as "10.0.0.1/24". Multiple IP addresses can be specified like this:
ipaddrs="10.0.0.1/24 10.0.0.2/24"
Note that in some cases, you may choose to not specify ipaddr or ipaddrs for a bridge template. That is allowed. If you don't want to specify an IP address for a regular interface, you can choose to use the interface template without an IP address specified in the config, or use the interface-noip template instead, for the sake of clarity.
Also note that if you specify multiple IP addresses, ifconfig will only show the first IP address. To view all IP addresses associated with the interface, use the ip addr show command.
General Variables
The following variables are enabled by default for all network scripts, and if specified will trigger a corresponding configuration action: nameservers: Set DNS nameservers using OpenResolv. Specify multiple nameservers like this: "1.2.3.4 1.2.3.5 1.2.3.6"
- domain: Set DNS domain using OpenResolv.
- gateway: Define a default IP gateway.
- route: Specify a semi-colon delimited list of routes to apply when this interface is brought up. Will be appended to ip route add.
- mtu: Set Maximum Transmit Unit for the interface
- slaves: Set slave interfaces of this interface (for bridges, etc.) All slaves will automatically be depended upon, and will also automatically have their mtu set to that of the current interface, if an mtu is specified for the current interface. This setting is required for the bond template and optional for the bridge template.
VLAN Variables
VLAN support is enabled by default for all network configuration scripts. If a network script has a name in the format netif.ethX.Y, then it is assumed to be a VLAN interface referencing trunk ethX and VLAN ID Y. If you desire a custom name for your VLAN interface, you can name your interface whatever you'd like and specify the following variables in your interface config [file: file:]
- trunk: VLAN trunk interface, e.g. "eth0"
- vlan: VLAN id, e.g. "32"
OpenResolv and resolv.conf
For the network configuration above, OpenResolv will be used to set DNS information when the netif.eth0 is brought up. The OpenResolv framework will add entries to /etc/resolv.conf, and will also handle removing these entries when the interface is brought down. This way, /etc/resolv.conf should always contain current information and should not need to be manually edited by the system administrator. dhcpcd will use OpenResolv for updating system DNS information as well.
Network-Dependent Services
One important difference between Gentoo Linux and Funtoo Linux is that, in Funtoo Linux, network-dependent services only strictly depend on netif.lo. This means that if another network service requires an interface to be up, such as samba requiring eth0, then the system administrator must specify this relationship by adding the following line to /etc/conf.d/samba:
rc_need="netif.eth0"
This will have the effect of ensuring that netif.eth0 is started prior to samba and that samba is stopped prior to stopping netif.eth0.
Many network services, especially those that listen on all network intefaces, don't need an rc_need line in order to function properly. Avoiding the use of rc_need when required will optimize boot times and allow more network services to remain available when network interfaces are brought up and down by the system administrator.
Multiple Network Configurations
For information on how to have multiple, independent network configurations, please see Stacked Runlevels.
Alternate Configs
If you need to run the same service with different configuration parameters depending upon runlevel, then you'll be happy to know that you can specify runlevel-specific conf.d files by appending a . <runlevel> suffix. In this particular example, we could imagine a situation where we had two child runlevels named home and work:
/etc/conf.d/netif.eth0.home /etc/conf.d/netif.eth0.work
Note that this feature works for all init scripts, not just network configuration scripts.
Interface Renaming
Funtoo network scripts now support interface renaming, so you can create an interface called lan if you would like. To so this, simply specify the MAC address of the interface you would like to rename using the macaddr variable: macaddr="00:15:17:19:b6:a3" If this MAC address is part of the netif.lan configuration file, then when this interface starts, whatever interface currently has the MAC address of 00:15:17:19:b6:a3 (i.e. eth5) will be renamed to lan prior to the interface being brought up, and will show up in ifconfig and ip commands as being an interface named lan.
Basic VLAN Configuration
The standard interface template supports VLANs. To use VLAN support, first configure the trunk interface using the interface-noip template. Assuming eth1 is trunked, you would create the file /etc/conf.d/netif.eth1 with the following contents:
template="interface-noip"
Then, create a network interface symlink for the trunk and add it to your default runlevel:
# cd /etc/init.d # ln -s netif.tmpl netif.eth1 # rc-update add netif.eth1 default
Now, assuming you wanted to configure a VLAN of 32, you would create a config file named /etc/conf.d/netif.eth1.32 that looks something like this:
template="interface" ipaddr="1.2.3.4/24" gateway="1.2.3.1"# etc...
Then, create a VLAN network interface symlink and add it to your default runlevel:
# cd /etc/init.d # ln -s netif.tmpl netif.eth1.32# rc-update add netif.eth1.32 default
The Funtoo network configuration scripts will automatically recognize the filename netif.eth1.32 as being VLAN 32 of trunk interface netif.eth1.
When the VLAN interface is brought up, it will be named eth1.32.
Custom VLAN Names
However, sometimes you may want to turn off automatic file-based VLAN naming and give your VLAN interface a custom name, such as mgmt. To do this, you would set up the trunk interface in the exact same way as described above, but instead of creating a netif.eth1.32 interface, you would create a netif.mgmt interface, and specify vlan and trunk in the /etc/conf.d/netif.mgmt config file, as follows:
template="interface" vlan="32" trunk="eth1" ipaddr="1.2.3.4/24" gateway="1.2.3.1" # etc...
When you specify trunk and vlan in the interface config file, filename-based auto-detecting of VLAN ID and trunk is disabled. Both trunk and vlan must be specified -- you can't specify just one.
Then you would simply create a VLAN network interface symlink for netif.mgmt:
# cd /etc/init.d # ln -s netif.tmpl netif.mgmt # rc-update add netif.mgmt default
When the VLAN interface is brought up, it will be named mgmt.
More Complex Network Configuration
If the standard templates don't work for your needs, simply create a new template -- I recommend starting from the interface template for most things:
# cd /etc/netif.d # cp interface custom
You can now call whatever commands you need to /etc/netif.d/custom. The following shell functions can be defined in a network script:
netif_create
In netif_create, you should call any commands to create the interface if it does not yet exist.
netif_depend
In netif_depend, you can define dependencies, using the functions need and use.
netif_pre_up
In netif_pre_up, you can define network configuration actions to perform prior to bringing the interface up. You can also ensure certain variables are specified by calling require var1 [var2...] here.
netif_post_up
In netif_post_up, you can define network configuration actions to perform after bringing the interface up.
netif_pre_down
In netif_pre_down, you can define network configuration actions to perform prior to bringing the interface down.
netif_post_down
In netif_post_down, you can define network configuration actions to perform after bringing the interface down.
netif_destroy
In netif_destroy, you can call any commands necessary to destroy/delete the interface if it is dynamic in nature (tun/tap, etc.)
How It Works
You do not specify a function for actually bringing up the interface, because the template-based system does this for you. The template-based system also performs all normal actions for required for bringing an interface down, so only need to specify atypical actions that must be performed - such as removing child interfaces or destroying a bridge using brctl.
When you create your own network configuration template, the following capabilities are available for use automatically, as long as the appropriate variables are set in the /etc/conf.d/netif.<ifname> file,, without requiring any explicit steps on your part:
- DNS configuration using domain and nameservers config settings. OpenResolv is used automatically.
- VLAN configuration using auto-naming (netif.ethX.Y) or via custom naming with trunk and vlan config settings.
- Default gateway and route configuration using the gateway and route settings.
- MTU configuration using the mtu setting.
- Auto-depend (and auto-MTU configuration) of slave interfaces specified using slaves setting.
- Renaming of existing network interface (specify MAC address using macaddr setting).
To take advantage of this functionality, simply enable the appropriate variables.
All other necessary network configuration and dependency behavior should be defined using the netif_-prefix functions described above.
Wireless Configuration
Wireless network configuration requires additional steps to the ones outlined above.
For wireless networks, you will need to enable wireless extensions in your kernel, the appropriate wireless modules, and emerge wireless-tools:
# emerge wireless-tools
I also recommend you emerge wpa_supplicant. wpa_supplicant implements modern WPA/WPA2 wireless link-layer encryption, which is necessary for connecting to most modern password-protected wireless networks:
# emerge wpa_supplicant
After emerging, add to your default runlevel as follows:
# rc-update add wpa_supplicant default
802.11 Passphrases
The only remaining step is to use the wpa_passphrase utility to store hashed keys (passwords) that wpa_supplicant can use to connect to your favorite wireless networks. This is done as follows:
# wpa_passphrase jims-netgear >> /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf <enter your passphrase>
Now, when wpa_supplicant encounters an SSID of jims-netgear, it will use the password you entered to authenticate with this access point.
At this point, ensure that dhcpcd has been enabled in your current runlevel and type rc to start everything up. wpa_supplicant should be able to automatically associate with SSIDs in its config file, at which point dhcpcd will take over and acquire an IP address from a DHCP server. This should all happen seamlessly. Use the iwconfig command to see if you have successfully associated with an access point.
Wireless Firmware
Many wireless adapters will now have everything they need to work. However, if you have an Intel wireless adapter, then you may need to install the proper microcode for your device in addition to ensuring that the proper Intel Wireless kernel drivers are available. For my Intel Corporation PRO/Wireless AGN [Shiloh] Network Connection, I need to do the following:
# emerge net-wireless/iwl5000-ucode
udev (running by default) and the Linux kernel firmware loader support (CONFIG_FW_LOADER) will automatically load the microcode when needed.
Note that Gentoo and Funtoo provide different versions of the Intel microcode because the version you need will depend on the kernel you are using. For my RHEL5-based kernel, I had emerge an older version of the microcode to match what my kernel wireless driver was expecting by typing:
- emerge =net-wireless/iwl5000-ucode-5.4.0.11
This installed this file iwlwifi-5000-1.ucode which was required by my RHEL5-based kernel. Just typing emerge net-wireless-iwl5000-ucode installed iwlwifi-500-2.ucode, which my kernel could not use. Before I had the right version of the microcode, I saw an error like this when I viewed the kernel messages by typing dmesg: iwl5000: iwlwifi-5000-1.ucode firmware file req failed: Reason -2
This error message generally means "I can't find this file iwlwifi-5000-1.ucode that I'm looking for in /lib/firmware." With the proper firmware in place, then the wireless driver will be happy and wpa-supplicant can then bring the wireless interface up.
Set your root password
It's imperative that you set your root password before rebooting:
# passwd
Create a user account
Logging in as root is a bad idea on a Linux system. Before rebooting, create a user account for everyday use. Adjust the groups in the example below to match your needs. Some of them may not exist yet on your system. Replace '<user_name>' with the name your going to use for your everyday user. The '-m' option instructs useradd to create a home directory for your user. See the useradd manpage for more info.
useradd -m -G audio,cdrom,cdrw,floppy,usb,users,video,wheel -s /bin/bash <user_name>
Don't forget to set a password for your new user:
passwd <user_name>
Verify boot time services
You should verify that all of your needed services have been added to the appropriate runlevel.
eselect rc list | less
Scroll though the list and check. Example of things you might need to add:
- lvm if you use logical volumes
- Your system logger if you installed one
- hibernate-cleanup if you use tuxonice
- iptables
- dbus
Add anything you need with the following command:
eselect rc add <script> <runlevel>
First boot
Now is the time to leave chroot, to unmount Funtoo Linux partitions and files and to restart your PC. If you installed GRUB, you will get an option to launch Funtoo Linux. Otherwise you will get to your already installed Linux and you will have to update your GRUB menu.
Leave the chroot, change directory to /, and unmount your funtoo partitions. Adjust the unmount command to match your setup
exit cd / umount /mnt/funtoo/home /mnt/funtoo/boot /mnt/funtoo/dev /mnt/funtoo/proc /mnt/funtoo/usr/portage /mnt/funtoo
In case of LVM2 also: swapoff /dev/mapper/vg-swap, vgchange -a n , if not You will see: Device dmcrypt_root is busy. In case of luks: cryptsetup luksClose dmcrypt_root to close the container.
Restart
shutdown -r now